NAS 660; Heat Resistant Stainless Steel
Characteristics of NAS 660.
A precipitation hardening stainless steel, NAS 660 (SUH 660, UNS S66286) maintains superior strength at high temperatures up to 700℃. It is comparable to nickel base heat resistant alloy, therefore NAS 660 can replace nickel alloys up to this temperature range. We supply this product in sheet and strip forms.
Chemical Composition
Chemical composition of NAS 660 is shown in the following table. NAS 660 includes aluminum and titanium in order to precipitate γ' or gamma prime phase [Ni3(Al, Ti)] which gives strength at high temperatures. Also molybdenum, vanadium, and boron are included to contribute high temperature strength by solution hardening. The composition follows Japan standard of JIS G4312 SUH660 specification.
(%)
| - | C | Si | Mn | Ni | Cr | Mo | V | Al | Ti | B |
| SUH660 JIS Specification |
≦0.08 | ≦1.00 | ≦2.00 | 24.00~ 27.00 |
13.50~ 16.00 |
1.00~ 1.50 |
0.10~ 0.50 |
≦0.35 | 1.90~ 2.35 |
0.001~ 0.010 |
| NAS660 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 25.0 | 15.0 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.20 | 2.15 | 0.004 |
Physical Properties
| Density g/cm3 | 7.94 |
| Specific heat kJ/kg・K 40~700℃ | 0.460 |
| Melting point ℃ | 1371~1427 |
| Magnetic permeabilityμ | 1.01 |
| Temperature | Specific electrical resistance μΩ‐cm |
| 30℃ | 91 |
| 540℃ | 116 |
| 650℃ | 119 |
| 731℃ | 120 |
| 815℃ | 122 |
| Temperature | Thermal conductivity W/m・K |
| 150℃ | 15.0 |
| 300℃ | 17.8 |
| 500℃ | 21.8 |
| 600℃ | 23.8 |
| Temperature | Coefficient of thermal expansion 10-6/℃ |
| 21~100℃ | 16.8 |
| 21~500℃ | 17.7 |
| 21~650℃ | 17.4 |
| 21~750℃ | 18.5 |
| 21~900℃ | 19.4 |
| Temperature | Young's modulus (MPa) | Torsional modulus (MPa) |
Poisson’s ratio |
| 24℃ | 20.1×104 | 7.2×104 | 0.306 |
| 593℃ | 15.8×104 | 5.7×104 | 0.331 |
| 649℃ | 15.3×104 | 5.5×104 | 0.336 |
| 704℃ | 14.9×104 | 5.3×104 | 0.338 |
| 760℃ | 14.2×104 | 5.2×104 | 0.340 |
*Physical properties are for materials after solution heat treatment followed by aging treatment.
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties at room temperature
Example of mechanical properties is shown in the following table. They are in the range of JIS specification, and hardness becomes up to HV320 by aging following solution heat treatment. It is characterized by large amount of aging hardness.
| Grades | Heat treatment | 0.2% Proof stress (MPa) |
Tensile strength (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Hardness (HV) |
Remarks |
| SUH660 JIS Specification |
Solution heat treatment | - | ≦730 | ≧25 | ≦202 | Solution heat treatment condition Rapid cooling after 965~995℃ |
| Solution heat treatment + Aging treatment | ≧590 | ≧900 | ≧15 | ≧261 | Aging treatment condition Air cooling after 700~760℃×16h |
|
| NAS660 (4 mm thick) |
Solution heat treatment | 344 | 665 | 40.4 | 176 | 0.2% proof stress is for reference |
| Solution heat treatment + Aging treatment | 774 | 1099 | 24.6 | 318 |
High Temperature Short Term Tensile Strength
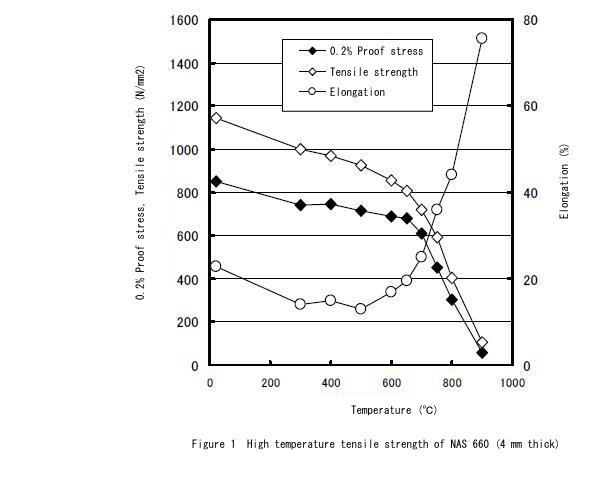
Examples of mechanical properties for 720℃×16hr Aging treated material are shown in Table 3 and Figure 1.
| Temperature (℃) |
0.2% Proof stress (MPa) |
Tensile strength (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
| 20 | 851 | 1143 | 22.8 |
| 300 | 739 | 998 | 14.0 |
| 400 | 743 | 967 | 14.8 |
| 500 | 715 | 926 | 13.0 |
| 600 | 690 | 857 | 16.8 |
| 650 | 678 | 809 | 19.4 |
| 700 | 609 | 719 | 24.9 |
| 750 | 450 | 593 | 36.0 |
| 800 | 301 | 403 | 44.0 |
| 900 | 55 | 104 | 75.6 |
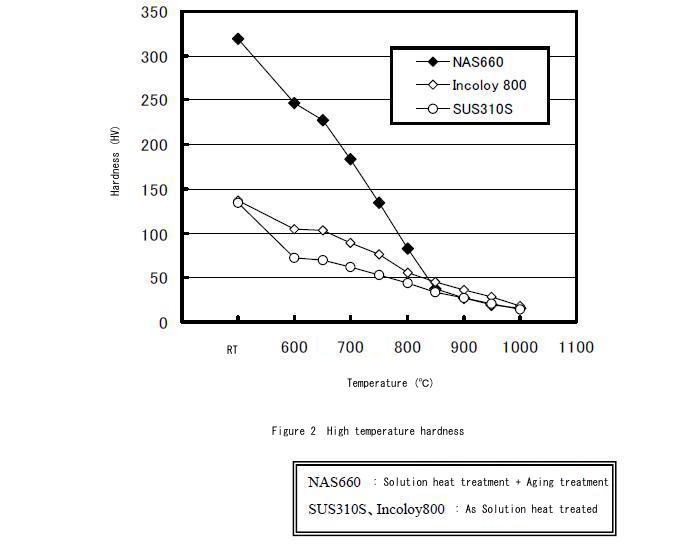
High Temperature Hardness
The following graph shows NAS 660 high temperature hardness in comparison with Type 310S stainless steel and Alloy 800. Up to 800℃ NAS 660 is harder which indicates better heat resistance than Alloy 800.
Creep Rupture Strength
Creep rupture strength of 720℃×16hr aging treated NAS 660 is shown in the following table.
| Temperature (℃) |
Rupture strength (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Creep strength 0.5% Total strain |
(MPa) 1.0% Total strain |
|
| 100hr Strength |
538 | 689 | 3 | 559 | 634 |
| 593 | 562 | 3 | 525 | 551 | |
| 649 | 434 | 5 | 365 | 414 | |
| 704 | 304 | 12 | 207 | 244 | |
| 732 | 241 | 28 | - | - | |
| 816 | 90 | 55 | - | - | |
| 1000 hr Strength |
538 | 599 | 3 | 537 | 585 |
| 593 | 490 | 3 | 469 | 482 | |
| 649 | 317 | 9 | 241 | 282 | |
| 704 | 207 | 24 | - | 155 | |
| 732 | 148 | 35 | - | - | |
| 816 | 58 | - | - | - |
Aging Hardening Behavior
The following graph shows 16 hours aging hardening behavior of NAS 660. The maximum hardness can be reached by aging treatment at around 700℃.
The second following graph shows the behavior depending on aging temperature and time for solution heat treated materials. Lower aging temperature requires long time for reaching maximum hardness, whilst higher aging temperature makes materials softer for short duration caused by over aging.
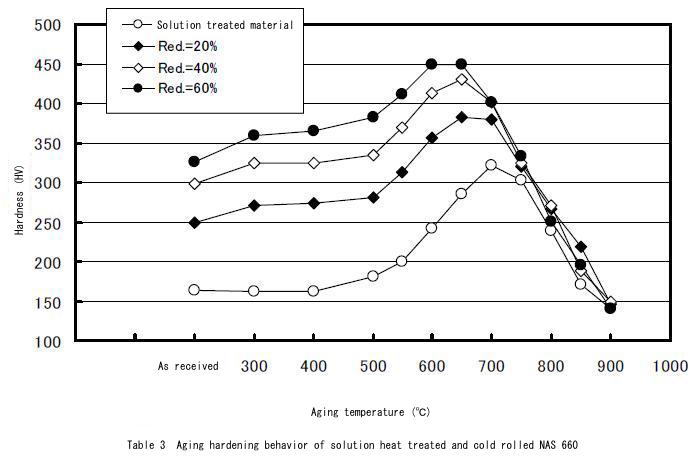
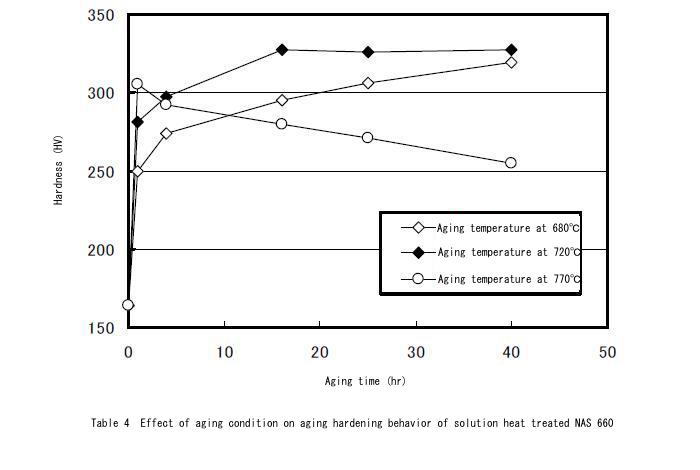
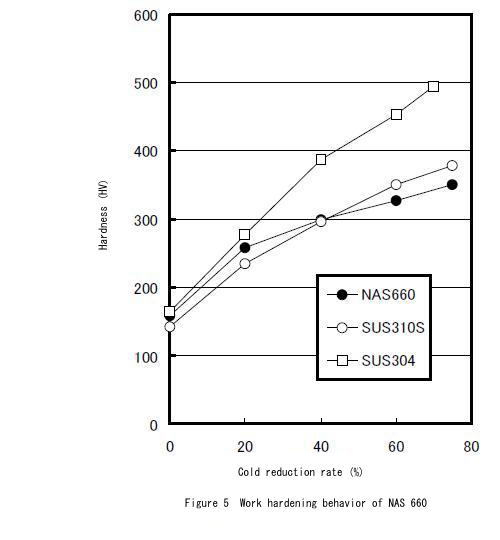
Work Hardening Behavior
Work hardening behavior is the same as Type 310S, therefore the same level of cold working is possible as Type 310S stainless steel.
Corrosion Resistance
NAS 660 provides superior corrosion resistance beyond the standard austenitic stainless steel SUS 304, and this does not vary even with thermal aging.
Corrosion resistance of NAS 660 (by JIS G 0577)
| Grades | Pitting potential (V) |
| NAS 660 * | 0.37 |
| NAS 660** | 0.38 |
| SUS 304 | 0.28 |
*: Solution heat treated, **: Solution heat treatment + thermal aging treatment
Test condition: 3.5% NaCl、30℃
Heat Treatment
NAS 660 is a precipitation hardening alloy. Its strength is increased and its properties emerge through aging after solution treatment. Two stages of heat treatment are generally carried out, as follows:
- Solution treatment at 980℃ followed by oil or water cooling
- Age hardening at 720℃ for 16 hours, followed by air cooling
For solution treatment cooling, either oil or water cooling is required, though air cooling is also suitable for thinner metal. Typically, NAS 660 is delivered with solution treatment already applied. By age hardening, strength is increased for accomplishing NAS 660 substantial property. Note that it is important to use a suitable temperature and holding time for aging to obtain the target strength.
Machinability
Compared to standard austenitic stainless steels, NAS 660 has somewhat superior machining properties. Although a high-speed steel tool can be used, we recommend the use of cemented carbide tools, and suggest combining a slower feed rate with a greater cutting depth.
Weldability
Spot, TIG, MIG and shield metal arc welding can be used on thin NAS 660 sheets under similar conditions to austenitic stainless steels. Also brazing is applicable in vacuum or dry pure hydrogen atmosphere.
Pickling
Descaling from NAS 660 by pickling is more difficult than standard austenitic stainless steel. However, alkaline molten salt helps descaling of this stainless steel. It is desirable to apply pickling as for standard austenitic stainless steel after alkaline molten salt treatment.
Application:
NAS 660 is an excellent choice when high-temperature strength is required such as jet engines, gas turbines and turbo charger components.

