NAS 185N; Corrosion Resistant Super Stainless Steel
Characteristics of NAS 185N.
A stainless steel with high chromium and high molybdenum content, NAS 185N (SUS 312L, UNS S31254) provides superior corrosion resistance in environments that are exceptionally corrosive such as high temperature seawater. Among the corrosion resistant stainless steel alloys on the market, NAS 185N is an economic choice with corrosion resistance comparable to nickel base alloys and pure titanium. We supply this product in plate, sheet and strip forms.
Designation/Standard
| NAS Specification | G4304/4305 | ASTM A240 | EN 10088-2/10028-7 |
| NAS 185N | SUS 312L | UNS S31254 | 1.4547 |
Chemical Composition
(%)
| - | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Mo | Cu | N |
| Specification (SUS 312L) |
≦0.020 | ≦0.80 | ≦1.00 | ≦0.030 | ≦0.015 | 17.50~ 19.50 |
19.00~ 21.00 |
6.00~ 7.00 |
0.50~ 1.00 |
0.16~ 0.25 |
| Specification (UNS S31254) |
≦0.020 | ≦0.80 | ≦1.00 | ≦0.030 | ≦0.010 | 17.5~ 18.5 |
19.5~ 20.5 |
6.0~ 6.5 |
0.50~ 1.00 |
0.18~ 0.22 |
Physical Properties
| Density g/cm3 | 8.02 |
| Specific heat J/(kg・k) 20℃ | 464 |
| Specific resistivity μΩ-cm | 88.2 |
| Thermal conductivity W/(m・k) | 12.3 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion 10-6/℃ 20~200℃ 20~300℃ 20~400℃ |
15.6 16.1 16.8 |
| Young's modulus MPa | 16.7x104 |
| Ferromagnetism | None | Melting point ℃ | 1360~1405 |
Crevice Corrosion Resistance
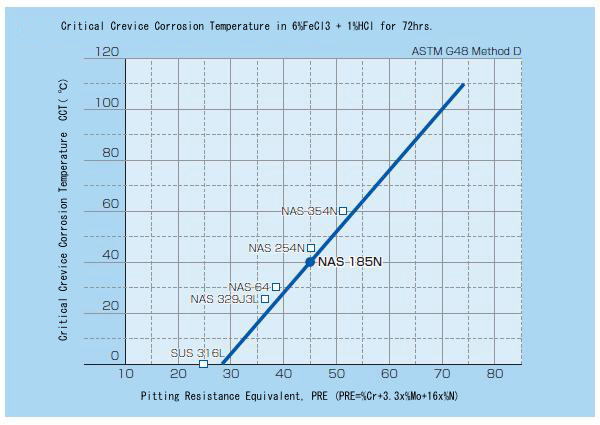
Crevice Corrosion Resistance
(Test method: U-bend specimen, in Boiling MgCl2 solution, for 300 hrs)
| Grades | Primary Components(wt%) | 45% (154℃) |
42% (142℃) |
40% (138℃) |
38% (134℃) |
35% (126℃) |
30% (115℃) |
25% (110℃) |
20% (108℃) |
| SUS 304 | 18Cr-8Ni | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | × |
| SUS 316L | 17Cr-12Ni-2Mo | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | ○ |
| NAS 64 | 25Cr-6Ni-3.3Mo-0.16N | × | × | × | × | × | × | ○ | ○ |
| NAS 155N | 18Cr-15Ni-4Mo-3Cu-0.15N | × | × | × | × | × | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| NAS 185N | 20Cr-18Ni-6Mo-0.8Cu-0.2N | × | × | × | × | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
○:Cracking ×:No-cracking
Mechanical properties
Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature
| 0.2% Proof stress (MPa) |
Tensile strength (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Hardness | |||
| (Hv) | (HRB) | |||||
| Specification of SUS 312L | ≧300 | ≧650 | ≧35 | ≦230 | ≦223 | |
| Specification of UNS S31254 | Sheet and strip | ≧310 | ≧690 | ≧35 | - | ≦223 |
| Plate | ≧310 | ≧655 | ≧35 | - | ≦223 | |
| Example of cold rolled sheet, 1.5 mm thick | 379 | 744 | 41 | 182 | - | |
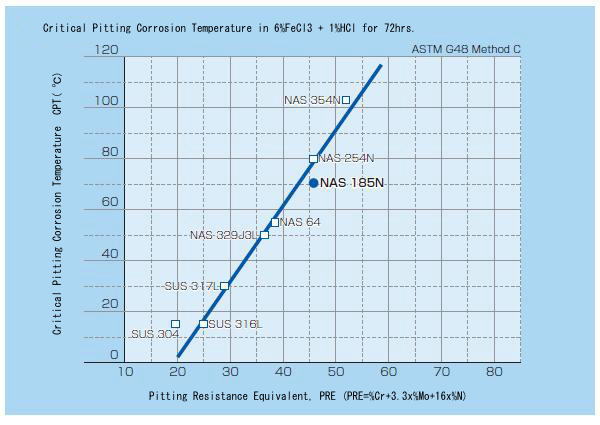
Corrosion Resistance
NAS 185N is high in both chromium and molybdenum content, which endow this stainless steel with excellent pitting corrosion and crevice corrosion resistance in high-chloride ion environments. Its high nickel content also provides exceptional stress corrosion cracking resistance.
Pitting Corrosion Resistance
Workability
Although NAS 185N can be hot- and cold-worked much like standard austenitic stainless steels such as Type 304 and Type 316, the high strength of the alloy must be kept in mind when doing so.
Weldability
NAS 185N can be shield metal arc welded, TIG welded and plasma welded much as any standard austenitic stainless steel. We recommend using Alloy C-276 type welding consumables with this product. Preheating and post-heating are not required.
Machinability
As with any stainless steel endowed with a high nickel content, machining NAS 185N is more challenging than standard austenitic stainless steels, though NAS 185N is more easily handled than nickel-based alloys. We recommend the use of a cemented carbide tool, and suggest combining a slower feed rate with a greater cutting depth.
Heat Treatment
As NAS 185N is an austenitic stainless steel, the same sort of heat treatment may be used as for standard austenitic stainless steels. In general, we suggest that NAS 185N be water cooled with a solution treatment between 1125 and 1175 ℃
Pickling
A mixture of nitric and hydrofluoric acids is used in pickling. To the extent that NAS 185 is more resistant to corrosion than SUS 304, descaling is more difficult. Alkaline immersion for a short time before acid pickling and shot blasting if possible are effective at descaling.
Application
・Seawater environments: desalination systems, seawater heat exchangers, condenser tubes
・High-chloride ion environments: pulp and paper mills, bleaching equipment
・Environments containing concentrated sodium chloride: plastic manufacturing equipment, chemical reactor vessels and tubing

